I like to look at what larger stationary woodworking tools looked like before the birth of electricity. So for today’s blog, I’m making you look at them too!
Large stationary tools which allow precision work did not appear with the birth of electricity. Though it may seem a table saw or band saw can only work off of an electrical motor, machines like these were common long before they needed to be plugged in. Running off of foot pedals, hand wheels, or a central axle driven by water, wind or steam power, these machines share many of the shapes, guards, rails and features of their electrical descendants.
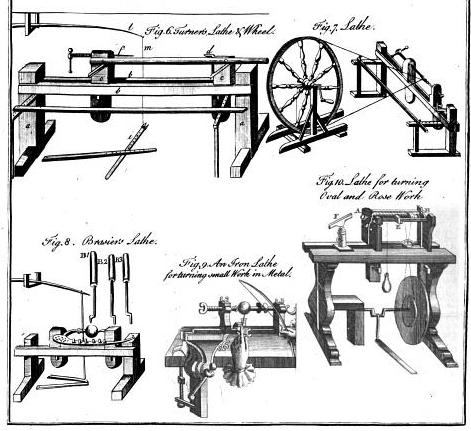
This is from The complete dictionary of arts and sciences, Volume 2, by Temple H. Croker, Thomas Williams, Samuel Clarke, published 1765.
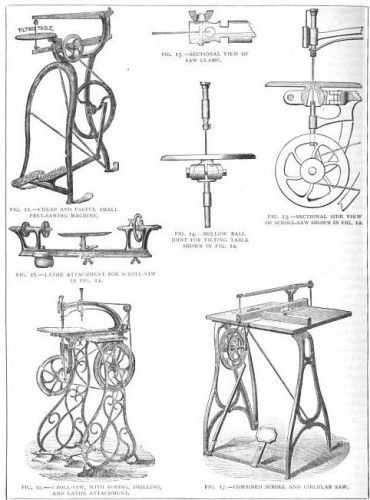
The next few are from Amateur work, illustrated, Volume 1, by Ward, Lock & Co., published 1883.
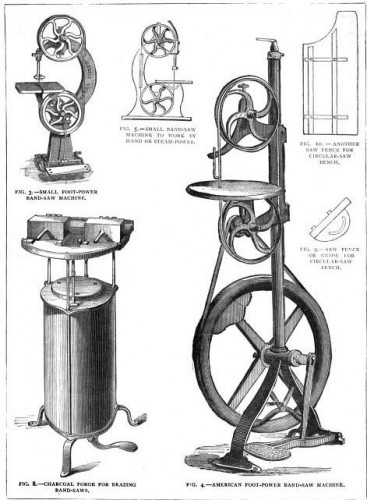
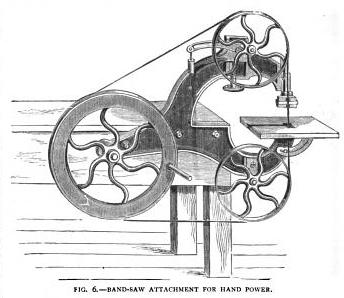
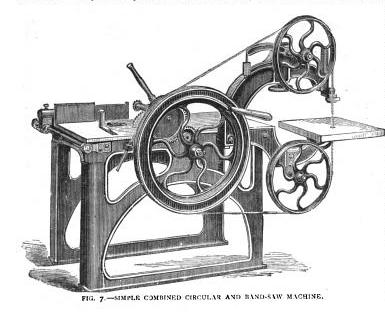
I imagine these kinds of tools took two people to operate; one on the wheel and one moving the material.
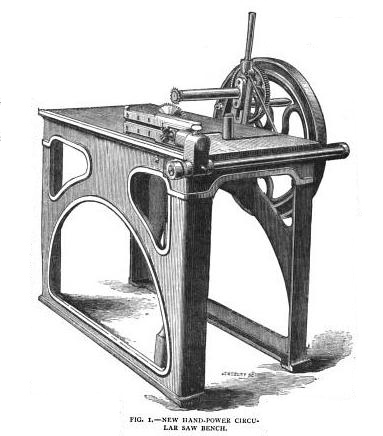
The following come from Wood workers’ tools catalogue, published by C.A. Stelinger & Co. in 1897.
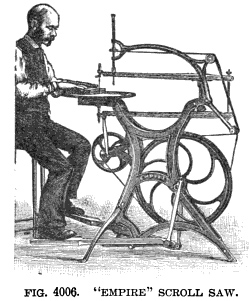
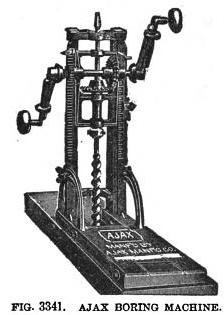
Imagine if you had to tell people that your job was to operate a boring machine all day.
