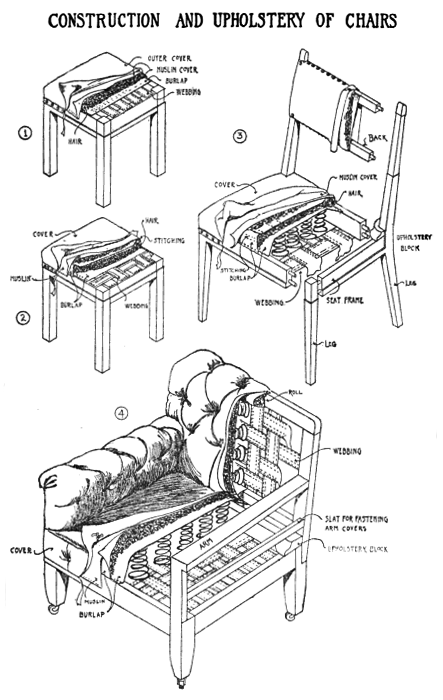
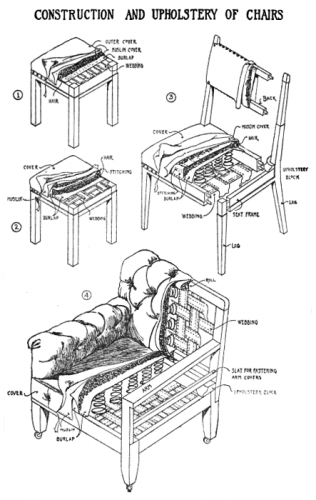
The following is a portion of an article which first appeared in The New York Times on June 7, 1903.
In the Spring of the year the scenery of plays that have failed in New York in the course of the Winter and the season which draws to a close may be found accumulated in a large storage warehouse far over on the west side of the city, in the locality of Twenty-eighth Street. This has served during many years as the chief mausoleum of the remains of these failures. The expenses of the interment include cartage at $5 a load, handling by the warehouse employes at $2 a load, and storage at $4 a load monthly. The acceptance states that settlement must be made quarterly, and that all goods held in arrears in payment twelve months will be seized and sold at auction. There is also the little bill for insurance which many an owner contracts with the fond hope that something may happen in the fire line before the year’s end.
In addition to this large place of storage there are a couple of rambling old stables on Thirteenth Street, east of First Avenue where much scenery that in the last half dozen years cost a snug fortune reposes in solid stacks awaiting the last judgement. In a small room of a neighboring scene painter are the models on view of the handsome interiors and exteriors piled away. Now and then somebody, harboring the notion of producing a play for trial at a nominal expense, drops in to examine this second-hand stock. Nothing results, however, satisfactory to any one concerned. The scenery representing picturesque mountain retreats and grottoes, on view once in a great spectacle, is a misfit for a domestic drama or a comedy. The nine scenes of a melodrama that sunk $6,500 are also of no use in the play, which requires new features up to date.
Mention should be made of the fact, though, that since the stock companies became more or less prosperous in and around New York, some small opportunity has come in sight to unload the scenery in storage. But such interest as there can be for the general reader in this statement must be stimulated by calling attention to the absurd difference between the cost of the scenery and its selling price. The manager, for instance, of two stock theatres in Brooklyn purchased not very long ago from a well-known player, who has given up being his own manager, five loads of scenery, nearly all new, and representing a cash outlay of almost $4,000, for $75. The cost of transportation across the bridge was $25 additional. There were seven wall-drops included in these loads, any one of which cost more originally than the whole purchase at second hand.
Originally published in The New York Times, June 7, 1903.